For developers, Windows 10 is a great place to run Docker Windows containers and containerization support was added to the the Windows 10 kernel with the Anniversary Update (note that container images can only be based on Windows Server Core and Nanoserver, not Windows 10). All that's missing is the Windows-native Docker Engine and some image. On Windows 10, after your docker container is started, you can run docker-machine ip in command line (cmd or Docker QuickStart Terminal, etc) to get the ip address of your docker container. This ip address is usually, 192.168.99.100. Description I am using Docker version 1.12.5 on Windows 10 via Hyper-V and want to use container executables as commands in the current path. I built a Docker image that is running fine, but I hav. It is now possible to run Docker containers on Windows 10 and Windows Server, leveraging Ubuntu as a hosting base. Imagine running your own Linux applications on Windows, using a Linux distribution you are comfortable with: Ubuntu! It is now possible to do so using the power of Docker technology and Hyper-V virtualization on Windows.
- Run Docker In Windows 10 Iso
- Run Docker In Windows 10 Home
- Run Docker In Windows 10 64
- Run Docker In Windows 10 64-bit
I admit it, I was not a friend of Oracle databases running in Docker containers for a long time. My database systems for testing and demo purposes were all running in VMware, Virtual Box or in the Oracle Cloud. But I have used the Windows Subsystem for Linux since beginning, to work with the Oracle Oracle Cloud Infrastructure CLI, Git Integration etc.. And what I really like is the WSL extension for Visual Studio Code which gives me to chance, to edit Ansible Vault files in Windows without any additional Linux based VM running.
With the update of the existing Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) architecture to version 2, the Docker Desktop for Windows is now fully integrated and able to run Docker container in WSL as a lightweight VM. Now it's time to change my mind, why not use Docker to try out new Oracle features, do some development stuff and more?
What to we need to run Oracle databases in WSL 2 Docker Containers?
- WSL 2
- Docker Desktop for Windows
- Docker images with an Oracle Database – I may use the images (oehrlis/docker) from my workmate Stefan Oehrli (oradba.ch)- merci vöumou
This blog post shows you how to setup WSL 2 to run Docker images. Sure, you can use the Oracle provided Docker images or self created images too. But I have verified the Oracle repository today, the Dockerfile version is 19.3.0. And I don't have the passion, to create new Dockerfiles for example to run 19.8 and download additional RU software.
The Docker menu in the top status bar indicates that Docker Desktop is running, and accessible from a terminal. If you've just installed the app, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
Installing Windows Subsystem 2 for Linux
Enable Windows Subsystem for Linux basic Functionality
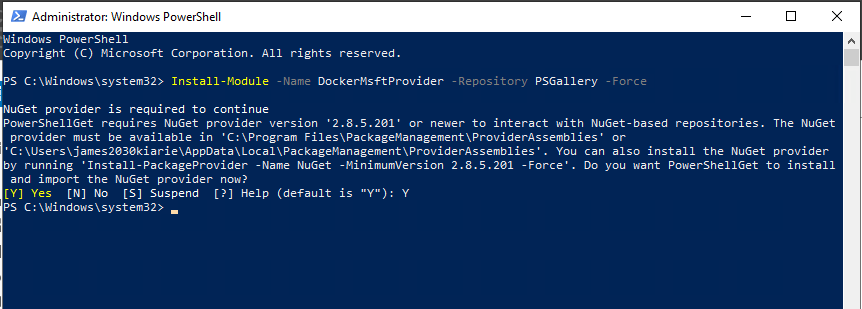
Start Windows PowerShell as Administrator and enable WSL.
dism.exe/online/enable-feature/featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform/all/norestart |
Restart the Windows machine. Now wsl.exe is available as command in Power Shell.
Set WSL 2 as default when installing Linux distributions from Microsoft Store like Ubuntu and SLES.
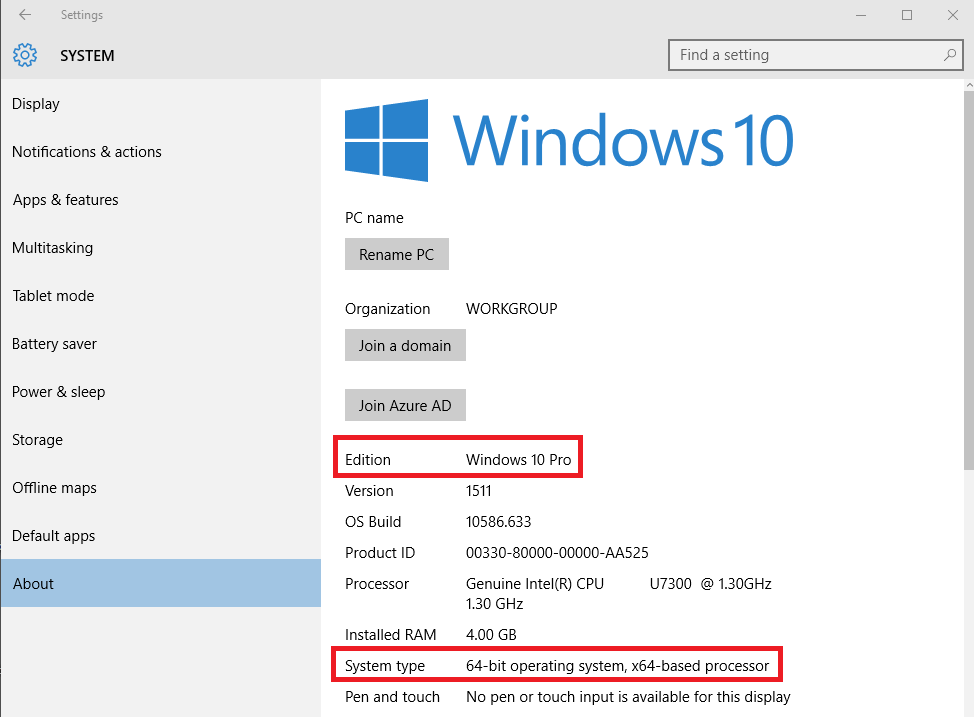
Getting Windows 10 ready for Docker
- https://code.visualstudio.com/blogs/2020/03/02/docker-in-wsl2
Install Docker Desktop for Windows
Run the Docker Desktop Installer executable. Let the checkboxes activated.
Two minutes later.
Start Docker and verify the Availability
After starting the Docker Desktop, you get a notification that Docker is starting. Docker is recognising that WSL is installed.
Docker is now ready to use.
Open a new PowerShell as Administrator and verify if docker and docker-compose are available.
Install Git
Link: https://git-scm.com/download/win
Run Docker In Windows 10 Iso
We use Git to checkout the Oracle docker containers later. There are several Git clients for Windows available. I use the one from git-scm.com. Just run the executable. After the successful installation, verify Git availability in PowerShell.
Go for the Oracle Database
Startup the Oracle Docker Image
Before cloning of the Git repository, I created a new directory in my Workplace folder.
Clone Docker Image Repository
The content of my cloned directory Oracle Database 19.0.0.0.
We use Docker Compose here, this makes it very easy to handle networking stuff like port forwarding. Example content of the docker-compose.yml file. In this case, I have not configured the Docker Volume Base, the files for the container are created in a subfolder of the clone directory.
Run Docker In Windows 10 Home
Your Mac must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop:
macOS must be version 10.14 or newer. That is, Mojave, Catalina, or Big Sur. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of macOS.
If you experience any issues after upgrading your macOS to version 10.15, you must install the latest version of Docker Desktop to be compatible with this version of macOS.
Note
Docker supports Docker Desktop on the most recent versions of macOS. That is, the current release of macOS and the previous two releases. As new major versions of macOS are made generally available, Docker stops supporting the oldest version and supports the newest version of macOS (in addition to the previous two releases). Docker Desktop currently supports macOS Mojave, macOS Catalina, and macOS Big Sur.
At least 4 GB of RAM.
VirtualBox prior to version 4.3.30 must not be installed as it is not compatible with Docker Desktop.
What's included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper.
Install and run Docker Desktop on Mac
Double-click
Docker.dmgto open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder.Double-click
Docker.appin the Applications folder to start Docker. (In the example below, the Applications folder is in 'grid' view mode.)The Docker menu in the top status bar indicates that Docker Desktop is running, and accessible from a terminal.
If you've just installed the app, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
Click the Docker menu () to seePreferences and other options.
Select About Docker to verify that you have the latest version.
Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop.
If you would like to rerun the tutorial, go to the Docker Desktop menu and select Learn.
Automatic updates
Starting with Docker Desktop 3.0.0, updates to Docker Desktop will be available automatically as delta updates from the previous version.
Run Docker In Windows 10 64-bit
When an update is available, Docker Desktop automatically downloads it to your machine and displays an icon to indicate the availability of a newer version. All you need to do now is to click Update and restart from the Docker menu. This installs the latest update and restarts Docker Desktop for the changes to take effect.
Uninstall Docker Desktop

Restart the Windows machine. Now wsl.exe is available as command in Power Shell.
Set WSL 2 as default when installing Linux distributions from Microsoft Store like Ubuntu and SLES.
Getting Windows 10 ready for Docker
- https://code.visualstudio.com/blogs/2020/03/02/docker-in-wsl2
Install Docker Desktop for Windows
Run the Docker Desktop Installer executable. Let the checkboxes activated.
Two minutes later.
Start Docker and verify the Availability
After starting the Docker Desktop, you get a notification that Docker is starting. Docker is recognising that WSL is installed.
Docker is now ready to use.
Open a new PowerShell as Administrator and verify if docker and docker-compose are available.
Install Git
Link: https://git-scm.com/download/win
Run Docker In Windows 10 Iso
We use Git to checkout the Oracle docker containers later. There are several Git clients for Windows available. I use the one from git-scm.com. Just run the executable. After the successful installation, verify Git availability in PowerShell.
Go for the Oracle Database
Startup the Oracle Docker Image
Before cloning of the Git repository, I created a new directory in my Workplace folder.
Clone Docker Image Repository
The content of my cloned directory Oracle Database 19.0.0.0.
We use Docker Compose here, this makes it very easy to handle networking stuff like port forwarding. Example content of the docker-compose.yml file. In this case, I have not configured the Docker Volume Base, the files for the container are created in a subfolder of the clone directory.
